Lane Line Detection
A pipeline used to identify the lane boundaries in a video from a front-facing camera on a car.

Overview
The steps of this project are follows:
- Compute the camera calibration matrix and distortion coefficients with a set of chessboard images.
- Apply a distortion correction to raw images.
- Use color transforms, gradients, etc., to create a thresholded binary image.
- Apply a perspective transform to rectify binary image (“birds-eye view”).
- Detect lane pixels and fit to find the lane boundary.
- Determine the curvature of the lane and vehicle position with respect to center.
- Warp the detected lane boundaries back onto the original image.
- Output visual display of the lane boundaries and nuemerical estimation of lane curvature and vehicle position.
Tech Stack
- Python
- NumPy
- Scipy
- OpenCV
Camera calibration using chessboard images
A set of chessboard images photographed at different angles were used for this purpose.
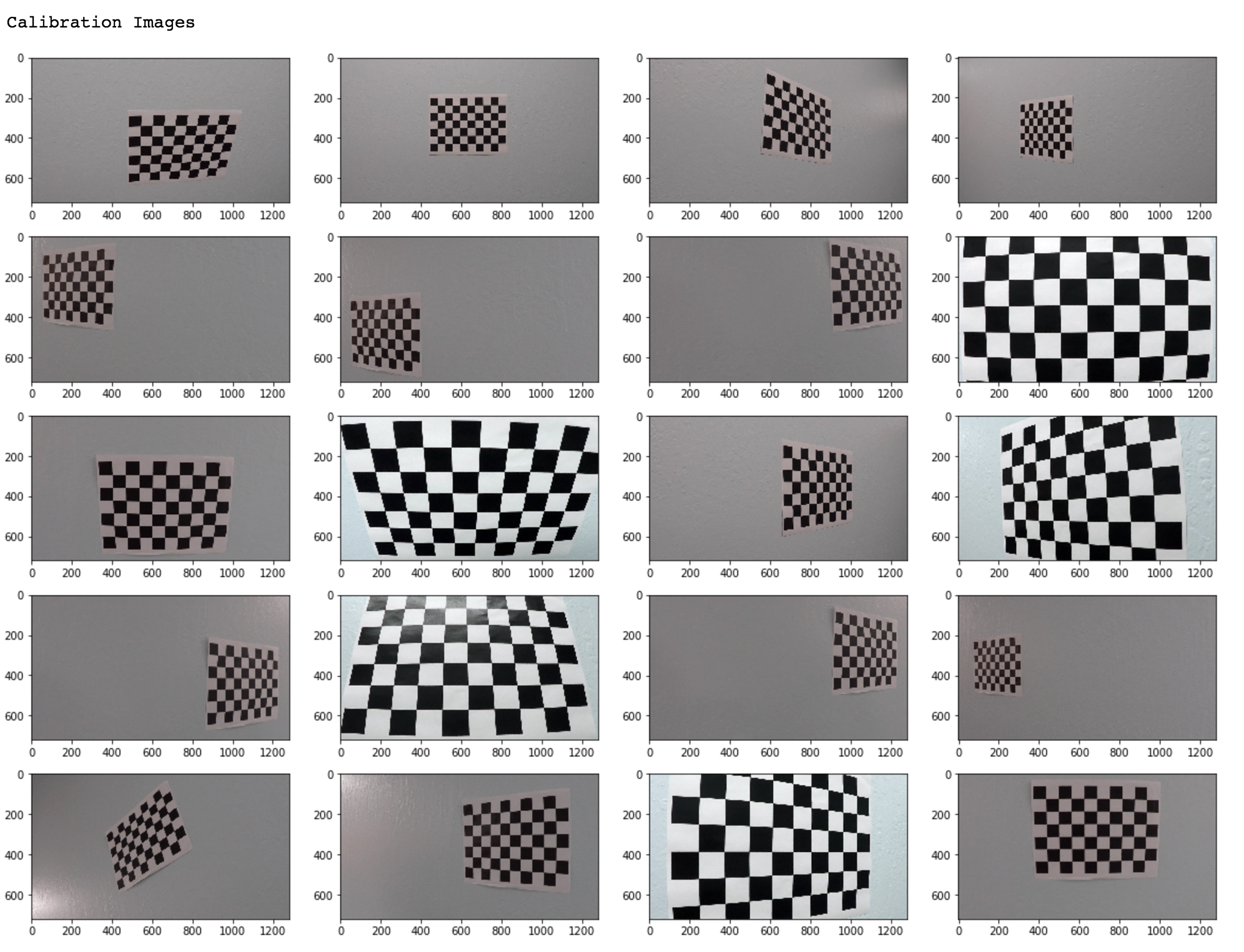
There are two types of distortion in this set of calibration images.
| Tangential | Radial |
|---|---|
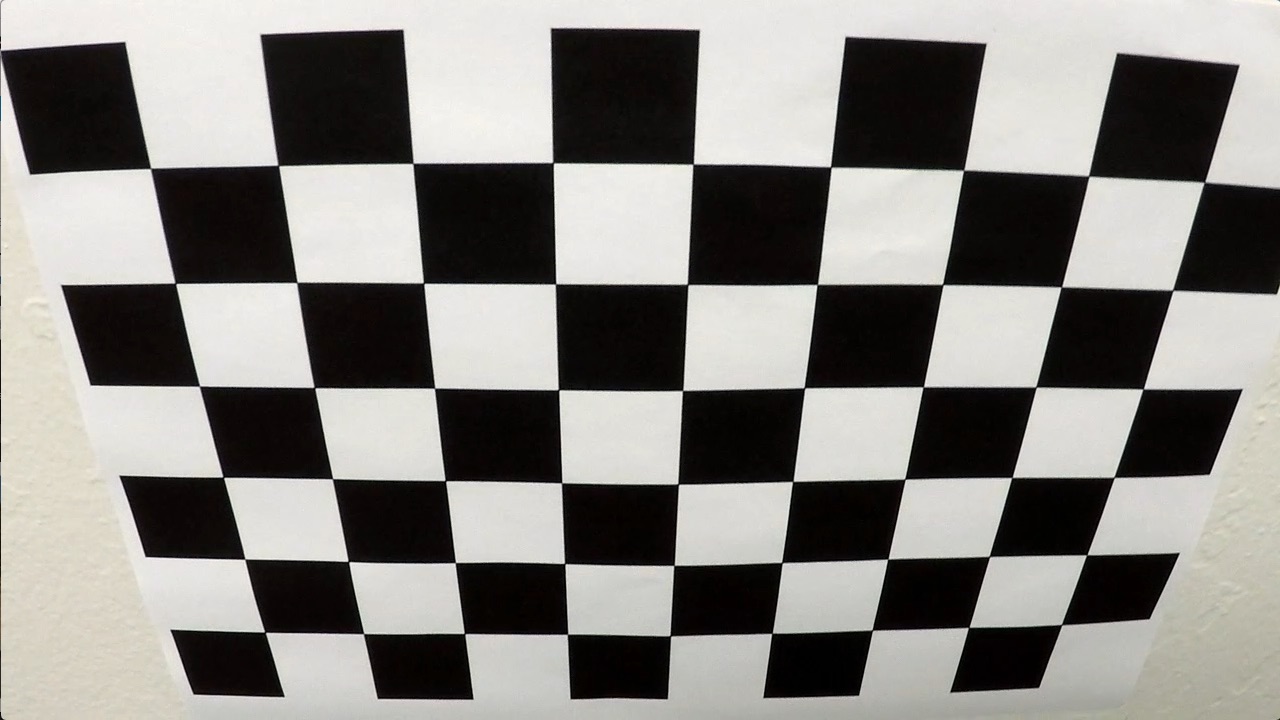 |
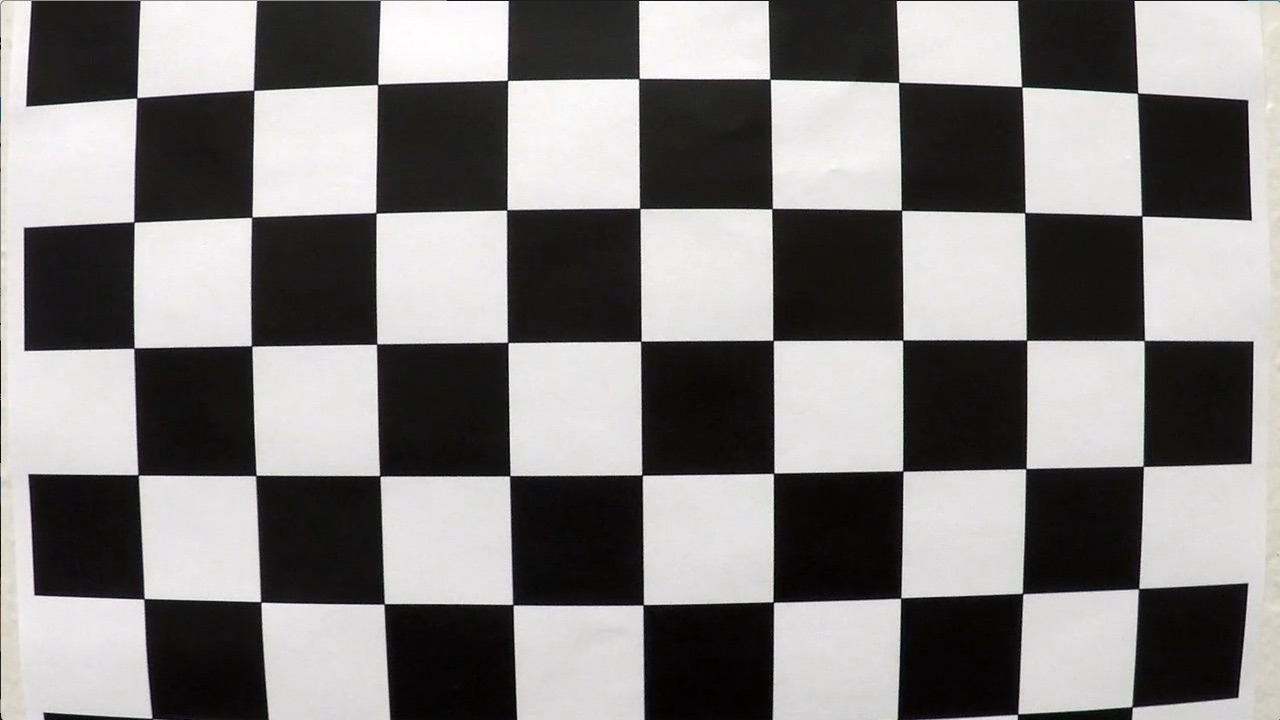 |
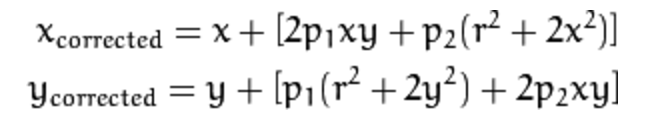 |
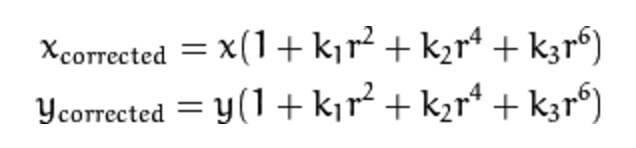 |
So for each image path:
- image is converted to grayscale using
cv2.cvtColor() - chessboard corners are found using
cv2.findChessboardCorners()
Once the chessboard corners are found, cv2.calibrateCamera() is called to obtain the calibration value that will be used to undistort our video images.
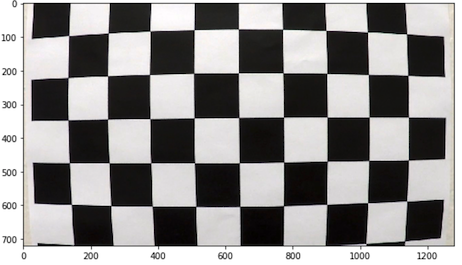
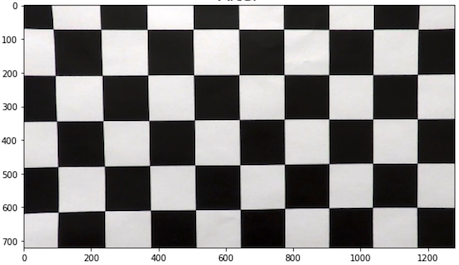
Distortion correction
Using cv2.undistort, the chessboard images can be undistorted.
| Original | Corrected |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Thresholded binary image
Filters used:
- Gradient on x and y axis with sobel filter size of 5
- HSV for yellow lane lines
- RGB for white lane lines
- S channel with a mask to suppress shadow
These thresholds are combined using logical OR.
| Original | Thresholded |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Perspective transform
From an image frame, coordinates are selected in the shape of a trapezoid. The destination coordinates, in the shape of a rectangle, are selected. Using cv2.getPerspectiveTransform, perspective transform M and inverse perspective transform Minv are calculated, which then will be used for image transformation.
def transform_image(img,size,src,dst):
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(src,dst)
Minv = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(dst,src)
warped_image = cv2.warpPerspective(img,M,size,flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
return warped_image, M, Minv
| Original | Transformed |
|---|---|
 |
 |
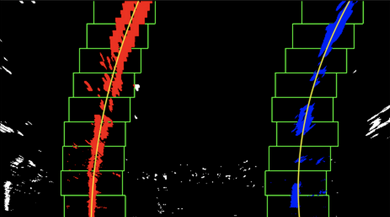
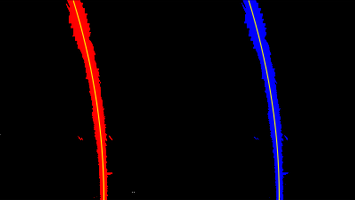
Finding lane lines
Using scipy.signal’s find_peaks_cwt() lane line pixels are calculated. Then using sliding window search, found peaks are then connected to form lines.
| Sliding Window Search | Peaks Connected |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Finding curvature and vehicle position
The curvature of 2nd order polnomial can be calculated with:
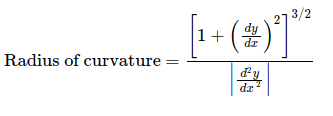
def curvature_radius (leftx, rightx, img_shape, xm_per_pix=3.7/800, ym_per_pix = 25/720):
ploty = np.linspace(0, img_shape[0] - 1, img_shape[0])
leftx = leftx[::-1] # Reverse to match top-to-bottom in y
rightx = rightx[::-1] # Reverse to match top-to-bottom in y
# Fit a second order polynomial to pixel positions in each lane line
left_fit = np.polyfit(ploty, leftx, 2)
left_fitx = left_fit[0]*ploty**2 + left_fit[1]*ploty + left_fit[2]
right_fit = np.polyfit(ploty, rightx, 2)
right_fitx = right_fit[0]*ploty**2 + right_fit[1]*ploty + right_fit[2]
# Define conversions in x and y from pixels space to meters
ym_per_pix = 25/720 # meters per pixel in y dimension
xm_per_pix = 3.7/800 # meters per pixel in x dimension
# Fit new polynomials to x,y in real space
y_eval = np.max(ploty)
left_fit_cr = np.polyfit(ploty*ym_per_pix, leftx*xm_per_pix, 2)
right_fit_cr = np.polyfit(ploty*ym_per_pix, rightx*xm_per_pix, 2)
# Calculate the new radii of curvature
left_curverad = ((1 + (2*left_fit_cr[0]*y_eval*ym_per_pix + left_fit_cr[1])**2)**1.5) / np.absolute(2*left_fit_cr[0])
right_curverad = ((1 + (2*right_fit_cr[0]*y_eval*ym_per_pix + right_fit_cr[1])**2)**1.5) / np.absolute(2*right_fit_cr[0])
# Curvature and radius in meters
return (left_curverad, right_curverad)
With the average of the two polynomials (bottom portion), mid point is calculated to determine the vehicle’s position since the camera is assumed to be attached in the middle of the vehicle.
Warp onto the original image
To draw the boundaries onto the original image:
- Curves are drawn on a blank image.
- Lane area is drawn by invoking
cv2.fillPoly(). - Using the inverse perspective matrix Minv, the lane area will be warped onto the original image space.
| Original | Lane Area Drawn |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Completed pipeline